The following rules will help you determine if you are eligible to claim the lifetime learning credit on your tax return.
Who Cannot Claim the Credit?
You cannot claim the lifetime learning credit if any of the following apply.
- Your filing status is married filing separate return.
- You are listed as a dependent in the Exemptions section on another person's tax return (such as your parents'). See Who Can
Claim a Dependent's Expenses, later.
- Your modified adjusted gross income is $50,000 or more ($100,000 or more in the case of a joint return). Modified adjusted gross income is
explained later under Does the Amount of Your Income Affect the Amount of Your Credit?
- You (or your spouse) were a nonresident alien for any part of 2001 and the nonresident alien did not elect to be treated as a resident
alien. More information on nonresident aliens can be found in Publication 519,
U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens.
- The eligible student received a tax-free withdrawal from a Coverdell ESA during 2001 and did not waive the tax-free treatment. This waiver
is discussed in chapter 4 under Waiver of Tax-Free Treatment.
- You claim the Hope credit for the same student in 2001.
Who Can Claim the Credit?
Generally, you can claim the lifetime learning credit if you pay qualified tuition and related expenses of higher education for an
eligible student who is either yourself, your spouse, or a dependent for whom you claim an exemption on your tax return.
Qualified tuition and related expenses are defined later under What Expenses Qualify? Eligible students are defined later under Who Is
an Eligible Student?
Dependent for whom you claim an exemption.
You claim an exemption for a person if you list his or her name on line 6c, Form 1040 (or Form 1040A).
Who Can Claim a Dependent's Expenses?
If there are higher education costs for your dependent for a year, either you or your dependent, but not both of you, can claim a lifetime learning
credit for that dependent's expenses for that year.
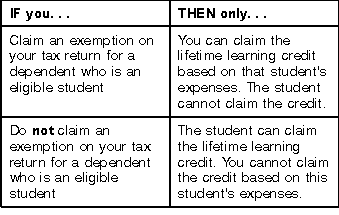
Expenses paid by dependent.
If you claim an exemption on your tax return for an eligible student who is your dependent, treat any expenses paid by the student as if you had
paid them. Include these expenses when figuring the amount of your lifetime learning credit.
 Qualified tuition and related expenses paid directly to an eligible educational institution for your dependent under a court-approved divorce
decree are treated as paid by your dependent.
Qualified tuition and related expenses paid directly to an eligible educational institution for your dependent under a court-approved divorce
decree are treated as paid by your dependent.
Expenses paid by others.
If someone other than you, your spouse, or your dependent (such as a relative or former spouse) makes a payment directly to an eligible educational
institution to pay for an eligible student's qualified tuition and related expenses, the student is treated as receiving the payment from the other
person. The student is treated as paying the qualified tuition and related expenses to the institution. If you claim an exemption on your tax return
for the student, you are considered to have paid the expenses.
Example.
Ms. Allen makes a payment directly to an eligible educational institution in 2001 for her grandson Todd's qualified tuition and related expenses.
For purposes of claiming a lifetime learning credit, Todd is treated as receiving the money as a gift from Ms. Allen and, in turn, paying his
qualified tuition and related expenses himself.
Unless an exemption for Todd is claimed on someone else's return, only Todd can use the payment to claim a lifetime learning credit.
If anyone else, such as his parents, claims an exemption for him on their tax return, whoever claims the exemption may be able to use the expenses
to claim a lifetime learning credit. In this case, Todd cannot claim a lifetime learning credit.
Who Is an Eligible Student?
For purposes of the lifetime learning credit, an eligible student is a student who is enrolled in one or more courses at an eligible
educational institution.
Eligible educational institution.
An eligible educational institution is any college, university, vocational school, or other postsecondary educational institution eligible to
participate in a student aid program administered by the Department of Education. It includes virtually all accredited, public, nonprofit, and
proprietary (privately owned profit-making) postsecondary institutions. The educational institution should be able to tell you if it is an eligible
educational institution.
Previous | First | Next
Publication Index | 2001 Tax Help Archives | Tax Help Archives | Home
